What is GSM in Mobile Communication?
In this tutorial, we are going to see What is GSM in Mobile Communication?
The GSM network (Global System for Mobile communications) is the most widely used cell phone standard in Europe at the beginning of the 21st century. It is a so-called “second generation” (2G) telephony standard because, unlike the first generation of cell phones, communications operate in an entirely digital mode.
Named “Groupe Spécial Mobile” at the beginning of its standardization in 1982, it became an international standard named “Global System for Mobile communications” in 1991.
In Europe, the GSM standard uses the 900 MHz and 1800 MHz frequency bands. In the United States, however, the frequency band used is 1900 MHz. Thus, we call tri-band (sometimes noted triband), cell phones can operate in Europe and the United States, and dual-band those operating only in Europe.
The GSM standard allows a maximum speed of 9.6 kbps, which allows the transmission of voice as well as digital data of low volume, for example, text messages (SMS, for Short Message Service) or multimedia messages (MMS, for Multimedia Message Service).
What is GSM in Mobile Communication?
Cell phone networks are based on the idea of cells, which are circular areas overlapping to cover a geographical area.
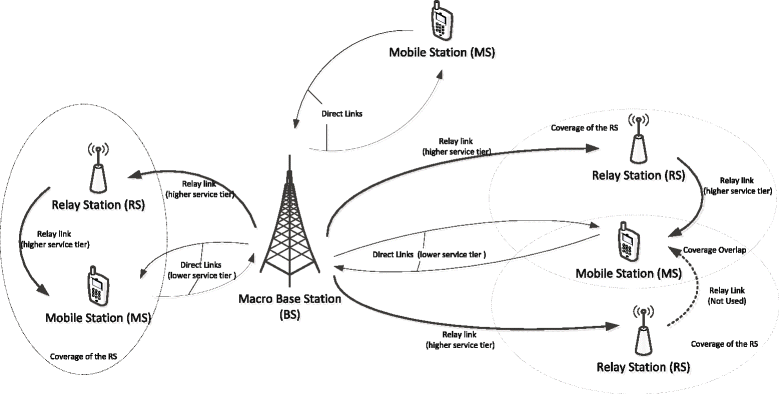
Image source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Fig-1-The-structure-of-the-RS-assisted-cellular-network.gif
Cellular networks are based on the use of a central transceiver at each cell, called a Base Station (BS) or Macro Base Station (MBS).
The smaller the distance between cells, the more bandwidth is available. Thus, in highly populated urban areas, cells with a size of a few hundred meters will be used while large cells of about thirty kilometers will cover rural areas.
In a cellular network, each cell is surrounded by 6 neighboring cells. To avoid interference, adjacent cells cannot use the same frequency. In practice, two cells with the same frequency range must be separated by a distance of two to three times the diameter of the cell.
In a GSM network, the user’s terminal is called a mobile station. A mobile station is composed of a SIM card (Subscriber Identity Module), which uniquely identifies the user, and a mobile terminal, meaning the user’s device (usually a cell phone).
The terminals (devices) are identified by a unique 15-digit identification number called IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity). Each SIM card also has a unique (and secret) identification number called IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity). This code can be protected with a 4-digit key called PIN code.
The SIM card allows identifying each user, independently of the terminal used during the communication with a base station. The communication between a mobile station and the base station is done through a radio link, generally called AIR interface.
SIM card:
A SIM card contains the following information:
- Subscriber’s telephone number (MSISDN)
- International mobile subscriber identity (IMSI)
- Status of the SIM card
- Service code (operator)
- Authentication key
- PIN code (Personal Identification Code)
- PUK code (Personal Unlock Code)





