Computer Network MCQ – DNS – Part 4
Networking MCQs questions with answers to prepare for exams, tests, and certifications. These questions are taken from a real written exam and some parts are taken from an interview. So you will find questions on CCNA, TCP/IP, Protocols, IP addressing issues, OSI model, and more. This MCQ will easily prepare anyone to pass their exam.
1. A host with the domain name pc1.room1.nasa.gov. is at _______ level in the DNS hierarchy tree. (The root is level one.)
A Third
B Fourth
C Fifth
D None of the above
2. DNS can use the services of ________ using port 53.
A UDP
B TCP
C Both A and B are true.
D None of the above
3. DNS can be described as an inversed hierarchical tree with a root node at the top and a maximum of ________.
A 128 levels
B 129 levels
C 130 levels
D 131 levels
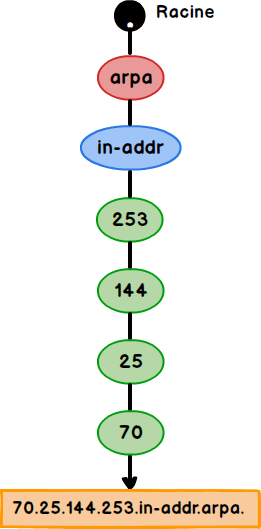
4. The domain used to map an IP address to a DNS name is called ________.
A Generic domains
B Reverse domain
C Primary domains
D Subdomains
5. The port used for encapsulation by the DNS server is ____.
A 80
B 443
C 23
D 53
6. A full domain name always ends with ______.
A 1 nœud
B 2 nœuds
C 0 nœud
D Null nœud
7. On the Internet, the domain name tree is divided into three ______.
A different steps
B different layers
C different components
D different sections
8. FQDN means ______.
A Filled Quality Domain Name
B Fully Qualified Domain Name
C First Qualified Domain Name
D False Quality Domain Name
9. xxx.yyy.com is a ______.
A PQDN
B DDNS
C FQDN
D All the answers are true
10. In the Domain Name System (DNS), a contiguous part of the entire tree is called ______.
A Host
B Server
C Domain
D Zone