UML Diagrams MCQs Questions With Answers – Part 31
Test your knowledge and boost your confidence with these multiple-choice quizzes focused on UML diagrams, foundational software engineering concepts, and real-world best practices. Designed for students, developers, and exam candidates, these MCQs offer a quick and effective way to assess your understanding and sharpen your skills.
1. What does the “opt” fragment model in a sequence diagram?
A An asynchronous call
B An optional condition (if)
C An iteration
D A conditional program termination
2. What does the “choice” pseudoterminal represent in a state diagram?
A A temporary action
B A decision point with multiple options
C A flow synchronization
D An automatic transition
3. In a recipe app, each ingredient can be used in multiple recipes. What relationship is this?
A Many-to-many association
B Composition
C Aggregation
D Dependency
4. How is a derived attribute written in UML?
A <<derived>> attributeName
B @attributeName
C /attributeName
D ?attributeName
5. You want to represent the logical sequence: “Authenticate → Choose action → Execute action”. Which diagram?
A Class diagram
B Activity diagram
C Component diagram
D State diagram
6. In a UML activity diagram, how do you model exception handling?
A With a transition to a final state
B With a decision node
C With a handler (exception node) linked to the activity
D With an alt loop
7. In a state diagram, what is a guard?
A A priority transition
B A blocking event
C A logical condition that must be true for the transition to occur
D An action performed during a transition
8. You’re developing a medical system. A prescription contains multiple medications, but medications can exist elsewhere. What kind of relationship is this?
A Composition
B Aggregation
C Association
D Dependency
9. What does the “alt” block represent here?

A It’s an exception
B It’s a condition with alternate branches
C It’s an iteration
D It’s a unit test
10. What does this arrow ..> mean?
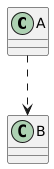
A A inherits from B
B B is a subclass of A
C A depends on B (without owning it)
D A contains B








